Thursday, Nov 15, 2018
Current Biology
Two Interlinked Bistable Switches Govern Mitotic Control in Mammalian Cells
Scott Rata, Maria F. Suarez Peredo Rodriguez, Stephy Joseph, Nisha Peter, Fabio E. Iturra, Fengwei Yang, Anotida Madzvamuse, Jan G. Ruppert, Kumiko Samejima, Melpomeni Platani, Monica Alvarez-Fernandez, Marcos Malumbres, William C. Earnshaw, Bela Novak, Helfrid Hochegger
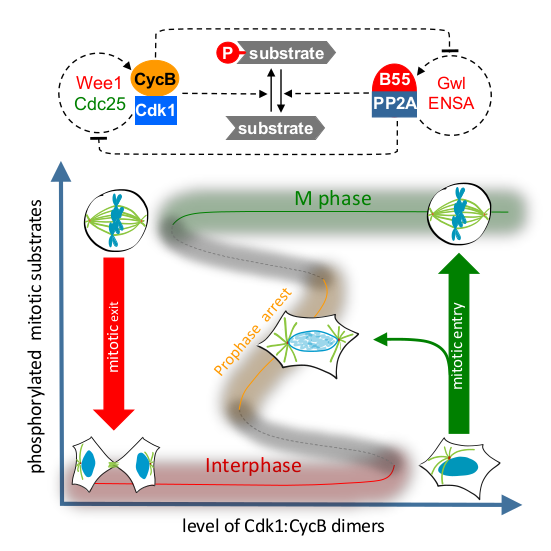
Distinct protein phosphorylation levels in interphase and M phase require tight regulation of Cdk1 activity [1,2]. A bistable switch, based on positive feedback in the Cdk1 activation loop, has been proposed to generate different thresholds for transitions between these cell-cycle states [3–5]. Recently, the activity of the major Cdk1-counteracting phosphatase, PP2A:B55, has also been found to be bistable due to Greatwall kinase-dependent regulation [6]. However, the interplay of the regulation of Cdk1 and PP2A:B55 in vivo remains unexplored. Here, we combine quantitative cell biology assays with mathematical modeling to explore the interplay of mitotic kinase activation a nd phosphatase inactivation in human cells. By measuring mitotic entry and exit thresholds using ATP-analog-sensitive Cdk1 mutants, we find evidence that the mitotic switch displays hysteresis and bistability, responding differentially to Cdk1 inhibition in the mitotic and interphase states. Cdk1 activation by Wee1/Cdc25 feedback loops and PP2A:B55 inactivation by Greatwall independently contributes to this hysteretic switch system. However, elimination of both Cdk1 and PP2A:B55 inactivation fully abrogates bistability, suggesting that hysteresis is an emergent property of mutual inhibition between the Cdk1 and PP2A:B55 feedback loops. Our model of the two interlinked feedback systems predicts an intermediate but hidden steady state between interphase and M phase. This could be verified experimentally by Cdk1 inhibition during mitotic entry, supporting the predictive value of our model. Furthermore, we demonstrate that dual inhibition of Wee1 and Gwl kinases causes loss of cell-cycle memory and synthetic lethality, which could be further exploited therapeutically.