Wednesday, Oct 24, 2018
PLOS Computational Biology
Dilution and titration of cell-cycle regulators may control cell size in budding yeast
Stefan Heldt, Reece Lunstone, John J. Tyson, Bela Novak
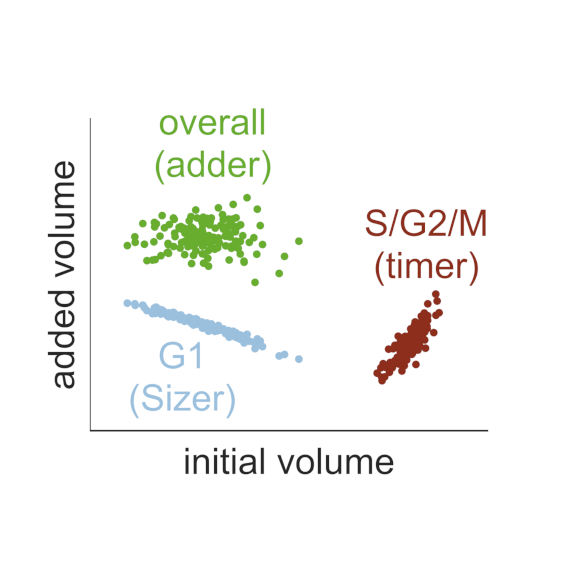
The size of a cell sets the scale for all biochemical processes within it, thereby affecting cellular fitness and survival. Hence, cell size needs to be kept within certain limits and relatively constant over multiple generations. However, how cells measure their size and use this information to regulate growth and division remains controversial. Here, we present two mechanistic mathematical models of the budding yeast (S. cerevisiae) cell cycle to investigate competing hypotheses on size control: inhibitor dilution and titration of nuclear sites. Our results suggest that an inhibitor-dilution mechanism, in which cell growth dilutes the transcriptional inhibitor Whi5 against the constant activator Cln3, can facilitate size homeostasis. This is achieved by utilising a positive feedback loop to establish a fixed size threshold for the START transition, which efficiently couples cell growth to cell cycle progression. Yet, we show that inhibitor dilution cannot reproduce the size of mutants that alter the cell’s overall ploidy and WHI5 gene copy number. By contrast, size control through titration of Cln3 against a constant number of genomic binding sites for the transcription factor SBF recapitulates both size homeostasis and the size of these mutant strains. Moreover, this model produces an imperfect ‘sizer’ behaviour in G1 and a ‘timer’ in S/G2/M, which combine to yield an ‘adder’ over the whole cell cycle; an observation recently made in experiments. Hence, our model connects these phenomenological data with the molecular details of the cell cycle, providing a systems-level perspective of budding yeast size control.